Avoiding dangerous diseases involves a combination of preventive measures and healthy lifestyle choices. Here are some tips to help reduce the risk of contracting dangerous diseases:
- Vaccinations: Stay up-to-date with vaccinations recommended by healthcare professionals. Vaccines can prevent various infectious diseases like measles, influenza, hepatitis, and more.
- Good Hygiene Practices: Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially before eating, after using the restroom, and after being in public places. Practice proper cough and sneeze etiquette by covering your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. A healthy diet supports a strong immune system, making your body better equipped to fight off infections.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen your immune system and improve overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritize getting enough sleep each night. Lack of sleep can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact the immune system. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time in nature.
- Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol: Smoking weakens the immune system and increases the risk of various diseases, including respiratory infections and certain cancers. Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive drinking can impair immune function.
- Practice Safe Sex: Use condoms and practice safe sex to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as HIV/AIDS, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about disease outbreaks and follow the guidelines provided by public health authorities. Be aware of travel advisories and take precautions when traveling to regions where certain diseases are prevalent.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider for preventive screenings and to monitor your overall health. Early detection and treatment of certain conditions can prevent them from becoming more serious.
Remember that prevention is key when it comes to avoiding dangerous diseases. By adopting healthy habits and following preventive measures, you can reduce your risk and promote overall well-being.
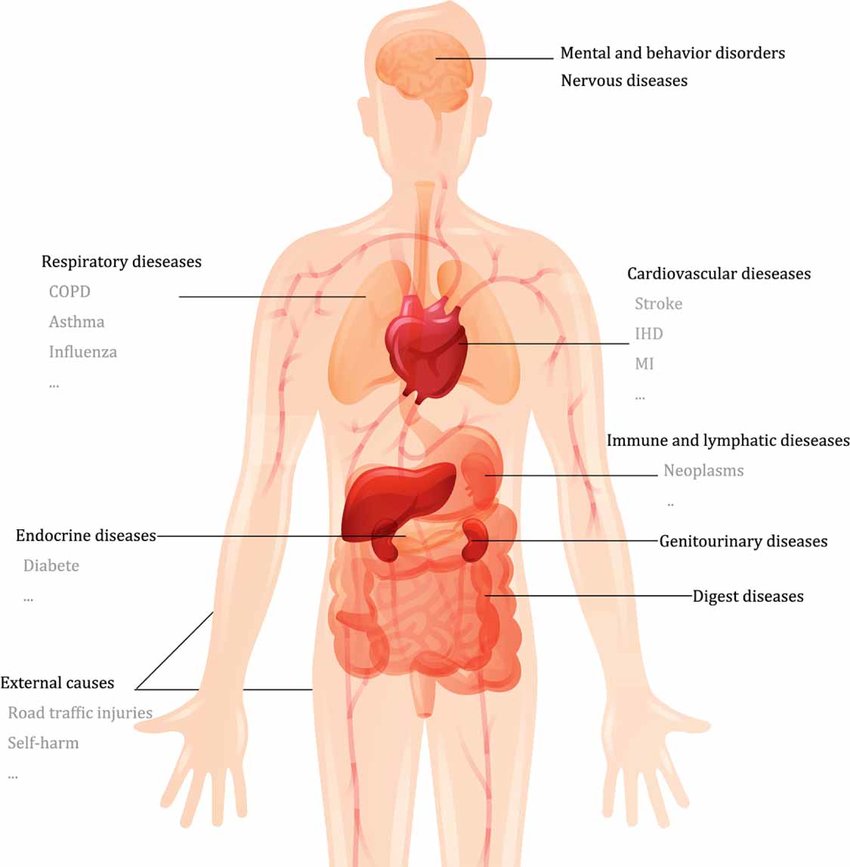
Dangerous Diseases
Certainly! Let’s delve deeper into specific diseases and how to avoid them:
- Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs):
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Monitor and control blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Respiratory Diseases (e.g., influenza, pneumonia, tuberculosis):
- Get vaccinated against influenza annually.
- Practice good respiratory hygiene, such as covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Avoid close contact with sick individuals.
- Follow guidelines for preventing airborne diseases, especially in crowded or poorly ventilated areas.
- HIV/AIDS and Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs):
- Practice safe sex by using condoms correctly and consistently.
- Get tested regularly for STIs, especially if you are sexually active or have multiple partners.
- Limit the number of sexual partners and choose partners who also practice safe sex.
- Avoid sharing needles or other injection equipment.
- Cancer:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Get screened for cancer regularly, following recommended guidelines for your age, sex, and risk factors.
- Protect yourself from excessive sun exposure to reduce the risk of skin cancer.
- Know your family history of cancer and discuss it with your healthcare provider.
- Diabetes:
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Eat a balanced diet with appropriate portion sizes and limit sugary foods and beverages.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly, especially if you have a family history of diabetes or other risk factors.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing diabetes, including medication, insulin therapy, and lifestyle changes.
- Vector-borne Diseases (e.g., malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus):
- Take precautions to avoid mosquito bites, such as using insect repellent, wearing long sleeves and pants, and sleeping under mosquito nets.
- Eliminate standing water around your home where mosquitoes breed.
- Follow travel advisories and take preventive measures when traveling to regions where vector-borne diseases are endemic.
- Liver Diseases (e.g., hepatitis B and C):
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis B if you are at risk (e.g., healthcare workers, individuals with multiple sexual partners).
- Practice safe sex and avoid sharing needles or other injection equipment to prevent hepatitis B and C transmission.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, which can increase the risk of liver damage and liver disease.
- Neurological Diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease):
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and cognitive stimulation.
- Manage chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and obesity, which can increase the risk of neurological diseases.
- Stay mentally and socially active, engaging in activities that stimulate the brain and maintain social connections.
- Autoimmune Diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus):
- Follow a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques.
- Avoid smoking, which can increase the risk of developing autoimmune diseases.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing autoimmune conditions, including medication and lifestyle changes.
- Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases (e.g., Ebola, Zika, COVID-19):
- Stay informed about disease outbreaks and follow guidelines provided by public health authorities.
- Practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and respiratory etiquette.
- Follow travel advisories and take precautions when traveling to regions where emerging infectious diseases are prevalent.
- Get vaccinated against preventable diseases and participate in public health efforts to control outbreaks.
By taking proactive steps to prevent these specific diseases and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, you can significantly reduce your risk and promote overall health and well-being.